|
Selected Publications Grouped by Topics Here's fairly comprehensive list of publications from our lab grouped by topics. When available, I have made links to download .pdf copies. Please email me (trexlerj@fiu.edu) if you would like copies of manuscripts lacking links. |
|
|
|
|
Community Ecology of the Everglades
Sokol,
E., J. M. Hoch, E. E. Gaiser, and J. C.
Trexler. Metacommunity structure along
resource and disturbance gradients in Everglades wetlands. Wetlands, in press
Goss, C. W., W. F. Loftus, and J. C.
Trexler. Fish
colonization of ephemeral wetlands in the Florida Everglades. Wetlands, in press
Gaiser, E. E., P. Sullivan, F. A. C. Tobias, A. J. Bramburger, and J.
C. Trexler. Boundary effects on benthic microbial
phosphorus concentrations and diatom beta diversity in a hydrologically-modified,
nutrient-limited wetland. Wetlands, in press.
Kline J. L., W. F. Loftus, K. Kotun, J. C. Trexler, J. S. Rehage, J. J. Lorenz, and M. Robinson. Recent fish introductions into Everglades National Park: An unforeseen consequence of water-management? Wetlands, in press
Lee, S., E. E. Gaiser, and J. C. Trexler. Diatom-based models for inferring hydrology
and periphyton abundance in a subtropical karstic
wetland: implications for ecosystem-scale bioassessment. Wetlands, in press
Harrison, E., J. Lorenz, and J. C. Trexler. Impacts of Mayan cichlids (Cichlasoma urophthalmus)
(Gunther) on native fish species in the oligohaline
Southern Everglades. Copeia, in press
Apodaca, J. J., J.
C. Trexler, N. Jue, M. Schrader, and J. Travis. 2013. Large-scale
natural disturbance alters genetic population structure of the sailfin molly, Poecilia latipinna. American Naturalist DOI: 10.1086/668831
Giacomini, H. C., D. L. DeAngelis, J. C. Trexler, and M. Petrere, Jr. 2012. Trait contributions
to fish community assembly emerge from trophic interactions in an
individual-based model. Ecological Modeling doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2012.12.003
Abbey-Lee, R., E. E. Gaiser, and J. C. Trexler. 2012. Relative role of dispersal dynamics and
competition in determining isotopic niche breadth. Freshwater Biology doi:10.1111/fwb.12084
Yurek, S, D. L. DeAngelis, J. C. Trexler, F. Jopp, and D. L. Donalson. 2012. Spatially explicit mechanistic model of
dynamic hydrology driving small fish biomass dispersal and stranding. Ecological Modeling, in press
Gaiser, E. E., J. C. Trexler, and P. R. Wetzel. 2012. Chapter 17. The Florida Everglades, pp 231-252. In: Batzer D. P., and A. H. Baldwin (eds) Wetland Habitats of North America: Ecology and Conservation Concerns. Berkeley: Univ. California Press.
Belicka, L. L., E. R. Sokol, J. M. Hoch, R. Jaffé, and J. C. Trexler. 2012. A molecular and stable isotopic approach to investigate the importance of algal and detrital energy pathways in a freshwater marsh. Wetlands 32:531-542. DOI 10.1007/s13157-012-0288-6
McElroy, T. C., K. L. Kandl, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Temporal population-genetic structure of eastern mosquitofish in a dynamic aquatic landscape. Journal of Heredity 102:678-687.
Sargeant, B. L., E. E. Gaiser, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Indirect and direct controls of macroinvertebrates and small fish by abiotic factors and trophic interactions in the Florida Everglades. Journal of Freshwater Biology 56:2334–2346.
Parkos, J. J., C. R. Ruetz III, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Disturbance regime and limits on benefits of refuge use for fishes in a fluctuating hydroscape. Oikos 120:1519-1530.
Ruehl, C. B., and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Comparisons of snail density, standing stock, and body size among freshwater ecosystems: A review. Hydrobiologia 665:1–13
Obaza, A., D. L. DeAngelis, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Using data from an encounter sampler to model fish dispersal. Journal of Fish Biology 78:495–513
Jopp, F., D. L. DeAngelis, J. C. Trexler. 2010. Modeling seasonal dynamics of small fish cohorts in fluctuating freshwater marsh landscapes. Landscape Ecology 25: 1041-1054.
DeAngelis, D. L., J. C. Trexler, C. Cosner, A. Obaza, and F. Jopp. 2010. Fish population dynamics in a seasonally varying wetland. Ecol. Modelling 221:1131-11
Sargeant, B., E. E. Gaiser, and J. C. Trexler. 2010. Biotic and abiotic determinants of community trophic diversity in an Everglades food web. Marine and Freshwater Ecology 61:11-22.
Doren, R. F., J. C. Trexler, A. D. Gottlieb, and M. Harwell. 2009. Ecological indicators for system-wide assessment of the Greater Everglades Ecosystem Restoration Program. Ecological Indicators 9:S2-S16
Trexler, J. C., and C. W. Goss. 2009. Aquatic fauna as indicators for Everglades restoration: Applying dynamic targets in assessments. Ecological Indicators 9S:S108-S119.
DeAngelis, D. L., J. C. Trexler, and D. D. Donalson. 2008. Food web dynamics
in a seasonally varying wetland. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering
5:877-887
Gaiser, E. E., J. H. Richards, J. C.
Trexler, R. F. Doren, P. V. McCormick, and S. Newman. 2008. Comment on
"Estimating ecological thresholds for phosphorus in the
Everglades." Environmental Science & Technology 42:6770-6771
Liston, S. E., S. Newman, and J. C.
Trexler. 2008. Macroinvertebrate community response to eutrophication in an
oligotrophic wetland: An in situ mesocosm
experiment. Wetlands 28:686-694
Chick, J. H., P. Geddes, and J. C.
Trexler. 2008. Periphyton mat structure mediates trophic interactions in a
subtropical wetland. Wetlands 28:378–389
Dorn, N., and J. C. Trexler.
2007. Crayfish assemblage shifts in a large drought-prone wetland: the roles of
hydrology and competition. Freshwater Biology 52, 2399–2411
Zambrano, L., E. Vázquez-Domínguez, D. García-Bedoya, W. F. Loftus, and J. C. Trexler. 2006. Fish community
structure in freshwater karstic wetlands of the
Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Ichthyological
Explorations 17:193-206
Green, D., J. C. Trexler, J.
Lorenz, C. McIvor, and T. Philippi. 2006. Spatial patterns of fish communities
along two estuarine gradients in southern Florida. Hydrobiologia
569:387-399 [Click
here to Download]
Williams, A. J., and J. C. Trexler. 2006. A preliminary analysis of the correlation of food-web characteristics with hydrology and nutrient gradients in the southern Everglades. Hydrobiologia 569: 493-504 [Click here to Download]
Rehage, J. S., and J. C. Trexler. 2006. Assessing the Net Effect of Anthropogenic Disturbance on Aquatic Communities in Wetlands: Community Structure Relative to Distance From Canals. Hydrobiologia 569:359-373 [Click here to Download]
Liston, S. E. 2006. Interactions between nutrient availability and hydroperiod shape macroinvertebrate communities in Florida Everglades marshes. Hydrobiologia 569:343-357 [Click here to Download]
Dorn, N. J., J. C. Trexler, and E. E. Gaiser. 2006. Exploring the role of large predators in marsh food webs: evidence for a behaviorally-mediated trophic cascade. Hydrobiologia 569:375-386 [Click here to Download]
Gaiser, E. E., D. L. Childers, R. D. Jones, J. H. Richards, L. J. Scinto and J. C. Trexler. 2006. Periphyton responses to eutrophication in the Florida Everglades: Cross-system patterns of structural and compositional change. Limnology and Oceanography 51:617-630 [Click here to Download]
Liston, S. E., and J. C. Trexler. 2005. Spatial and temporal scaling of macroinvertebrate communities inhabiting floating periphyton mats in the Florida Everglades. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24:832-844 [Click here to Download]
Trexler, J. C., W. F. Loftus, and S. Perry. 2005. Disturbance frequency and community structure in a twenty-five year intervention study. Oecologia 145:140-152 [Click here to Download now] electronic supplemental materials [Click here to Download now]
DeAngelis, D. L., J. C. Trexler, and W. F. Loftus. 2005. Life history trade-offs and community dynamics of small fishes in a seasonally pulsed wetland. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sci. 62:781-790 [Click here to Download now]
Dorn, N. J., R. Urgelles, and J. C. Trexler. 2005. Evaluating active and passive sampling methods to quantify crayfish density in a freshwater marsh. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24:346-356 [Click here to Download now]
Ruetz, C. R., III, J. C. Trexler, F. Jordan, W. F. Loftus, and S. A. Perry. 2005. Population dynamics of wetland fishes: Spatiotemporal patterns shaped by hydrological disturbance? Journal of Animal Ecology 74:322-332 [Click here to Download now]
Gaiser, E. E., J. C. Trexler, J. H. Richards, D. L. Childers, D. Lee, A. L. Edwards, L. J. Scinto, K. Jayachandran, G. B. Noe, R. D. Jones. 2005. Exposure to above-ambient phosphorus causes ecosystem state change in the Everglades. Journal of Environmental Quality 34: 717-723 [Click here to Download now]
Chick, J. H., C. R. Ruetz III, and J. C. Trexler. 2004. Spatial scale and abundance patterns of large fish communities in freshwater marshes of the Florida Everglades. Wetlands 24:652-664 [Click here to Download now]
Wolski, L. F., J. C. Trexler, E. B. Nelson, T. Philippi, and S. A. Perry. 2004. Assessing visitor impacts from long-term sampling of wetland communities in the Everglades. Freshwater Biology 49:1381-1390 [Click here to Download now]
Kobza, R. M., J. C. Trexler, W. F. Loftus, and S. A. Perry. 2004. Community structure of fishes inhabiting aquatic refuges in a threatened karstic wetland and its implication for ecosystem management. Biological Conservation, 116:153-165 [Click here to Download now]
Geddes, P., and J. C. Trexler. 2003. Uncoupling of omnivore-mediated positive and negative effects on periphyton mats. Oecologia 136:585-595. [Click here to Download now]
McElroy, T. C., L. L. Kandl, J. Garcia and J. C. Trexler. 2003. Extinction-colonization dynamics structure genetic variation of spotted sunfish (Lepomis punctatus) in the Florida Everglades. Molecular Ecology 12:355-368. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C., W. F. Loftus, and J. Chick. 2003. Setting and monitoring restoration goals in the absence of historical data: The case of fishes in the Florida Everglades, pp 351-376. In D. Busch and J. C. Trexler. Monitoring Ecoregional Initiatives: Interdisciplinary Approaches for Determining Status and Trends of Ecosystems. Island Press [Click here to Download now]
Taylor, R. C., J. C. Trexler, and W. F. Loftus. 2001. Separating the effects of intra- and interspecific age-structured interactions in an experimental fish assemblage. Oecologia 127: 143-152. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C., W. F. Loftus, F. Jordan, J. Lorenz, J. Chick, and R. M. Kobza. 2001. Empirical assessment of fish introductions in a subtropical wetland: an evaluation of contrasting views. Biological Invasions 2:265-277. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C., W. F. Loftus, C. F. Jordan, J. Chick, K. L. Kandl, T. C. McElroy, and O. L. Bass. 2001. Ecological scale and its implications for freshwater fishes in the Florida Everglades. Pp. 153 – 181, in J. W. Porter and K. G. Porter (eds.) The Everglades, Florida Bay, and Coral Reefs of the Florida Keys: An Ecosystem Sourcebook. CRC, Boca Raton. (Watch out, a big file... about 5 Megs). [Click here to Download now]
Turner, A. M., J. C. Trexler, F. Jordan, S. J. Slack, P. Geddes, and W. Loftus. 1999. Targeting ecosystem features for conservation: Standing crops in the Florida Everglades. Conservation Biology 13:898-911. [Click here to Download now]
Chick, J. H., S. Coyne, and J. C. Trexler. 1999. Effectiveness of airboat electrofishing for sampling fishes in shallow vegetated habitats. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 19:957-967
Jordan, C. F., S. Coyne, and J. C. Trexler. 1997. Sampling fishes in heavily vegetated habitats: the effects of habitat structure on sampling characteristics of the 1-m2 throw trap. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 126:1012-1020. [Click here to Download now]
Turner, A., and J. C. Trexler. 1997. Sampling invertebrates from the Florida
Everglades: a comparison of alternative methods. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16:694-709 [Click here to
Download now]
|
Top left: Throw-trap sampling in the Water Conservation Area 3A; Top right: One of three flumes used to study effects of phosphorus additions in the Everglades National Park; Bottom left: a Florida gar collected by airboat-mounted electorfishing; Bottom right: cages used to study biotic interactions in the Everglades food web. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Some other publications on environmental management
Busch, D. E. and J. C.
Trexler (Editors) 2003. Monitoring Ecosystems: Interdisciplinary
Approaches for Evaluating Ecoregional Initiatives.
Island Press.
Collins, T., J. C.
Trexler, L. G. Nico, and T. Rawlings.
2002. Genetic diversity in a morphologically conservative invasive taxon: Multiple
swamp eel introductions in the southeastern United States. Conservation
Biology 16:1024-1035. [Click here to Download
now]
Trexler, J. C., and J. Travis. 2000. Can marine protected areas conserve stock attributes? Bulletin of Marine Science 66:853-873 [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C. 1995. Restoration of the Kissimmee River: A conceptual
model of past and present fish communities and its consequences for evaluating
restoration success. Restoration Ecology 3:195-210 [Click
here to Download]
Some papers by my graduate students
(Most of these also appear in other lists on this page)
* MS student
**PhD student
Ruehl, C. B.**, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Comparisons of snail density, standing stock, and body size among freshwater ecosystems: A review. Hydrobiologia 665:1–13
Obaza, A.*, D. L. DeAngelis, and J. C. Trexler. 2011. Using data from an encounter sampler to model fish dispersal. Journal of Fish Biology 78:495–513
Liston**, S. E., S. Newman, and J. C. Trexler. 2008. Macroinvertebrate community response to
eutrophication in an oligotrophic wetland: An in situ mesocosm
experiment. Wetlands 28:686-694
Chick, J. H., P. Geddes*, and J. C.
Trexler. 2008. Periphyton mat structure mediates trophic
interactions in a subtropical wetland. Wetlands 28:378–389
Green,* D., J. C. Trexler, J. Lorenz, C. McIvor, and T. Philippi. 2006. Spatial patterns of fish communities along two estuarine gradients in southern Florida. Hydrobiologia 569:387-399
Williams*, A. J., and J. C. Trexler. 2006. A preliminary analysis of the correlation of food-web characteristics with hydrology and nutrient gradients in the southern Everglades. Hydrobiologia 569: 493-504
Liston**, S. E. 2006. Interactions between nutrient availability and hydroperiod shape macroinvertebrate communities in Florida Everglades marshes. Hydrobiologia 569:343-357
Liston**, S. E., and J. C. Trexler. 2005. Spatial and temporal scaling of macroinvertebrate communities inhabiting floating periphyton mats in the Florida Everglades. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24:832-844 [Click here to Download]
Kobza*, R. M., J. C. Trexler, W. F. Loftus**, and S. A. Perry. 2004. Community structure of fishes inhabiting aquatic refuges in a threatened karstic wetland and its implication for ecosystem management. Biological Conservation, In press [Click here to go to pre-print download site]
Geddes*, P., and J. C. Trexler. 2003. Uncoupling of omnivore-mediated positive and negative effects on periphyton mats. Oecologia 136:585-595. [Click here to Download now]
Taylor*, R. C., J. C. Trexler, and W. F. Loftus**. 2001. Separating the effects of intra- and interspecific age-structured interactions in an experimental fish assemblage. Oecologia 127: 143-152. [Click here to Download now]
Turner**, T. F. 2001. Comparative study of larval transport and gene flow in darters. Copeia 2001(3): 766-774.
Turner**, T. F., J. C. Trexler, J. L. Harris, and J. L. Haynes. 2000. Nested cladistic analysis indicates population fragmentation shapes genetic diversity in a freshwater mussel. Genetics 154:777-785. [Click here to Download now]
Schirripa**, M. J., and J. C. Trexler. 2000. Effects of mortality and gear selectivity on the otolith radius total length relation. Fisheries Research 46:83-89
Turner**, T. F., and J. C. Trexler. 1998. Ecological and historical associations of gene flow in darters (Teleostei: Percidae). Evolution 52:1781-1801
Turner**, T. F. 1997. Mitochondrial control region sequences and phylogenetic systematics of darters. Copeia 1997(2): 319-338.
Turner**, T. F., J. C. Trexler, D. Kuhn, and H. Robison. 1996. Life history variation and comparative phylogeography of darters (Pisces:Percidae) from the North American central highlands. Evolution 50:2023-2036
Turner**, T. F., J.C. Trexler, G.L. Miller, K. E. Toyer. 1994. Temporal and spatial dynamics of larval
and juvenile fishes in a temperate floodplain river. Copeia 1994: 174-183.
Some old papers on analysis of foraging data.
Trexler, J. C., and J. Travis. 1993. Nontraditional regression analyses. Ecology 74:1629-1637. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C.,
C. E. McCulloch, and J. Travis. 1988. How can the functional response
best be determined? Oecologia 76:206-214. [Click here to
Download]
|
Life history
and ecology of sailfin mollies (Poecilia latipinna) |
|
|
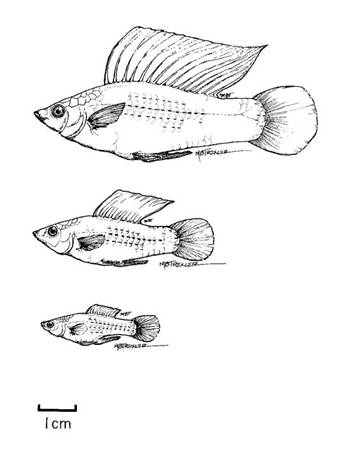
The following papers examine the biology of sailfin mollies, primarily exploring the mechanisms maintaining geographic variation in body size of male mollies. Individuals expressing the range of male size depicted to the right can be observed living together in many populations, but the frequency of the different sized males varies among populations. The variation among males in size primarily results from allelic variation of a single locus on the male sex chromosome that determines the timing of sexual maturation. Large males have different mating patterns than small males, and generally different demographic patterns, as revealed by our research. This has proven to be an interesting system to examine the balance between sexual selection and viability selection. My most recent work with this system has been to examine factors involved in evolution of female reproductive investment. We determined that female mollies display plasticity in the timing of their investment to a reproductive bout, potentially permitting an intermediate condition between lecithotrophy and matrotrophy. Lecithotrophic development indicates embryos nourished by yolk (energy stored before fertilization), while matrotrophic development describes embryos receiving supplemental nourishment during development beyond the yolk reserves. Livebearing fishes display a continuum of conditions from pure lecithotrophy to largely matrotophic nourishment. Papers listed below provide field descriptions and laboratory experiments into the pattern of investment, and a model exploring aspects of the environmental conditions favoring matrotrophy or lecithotrophy (early or late energetic investment in individual offspring as a potential trade-off with commitment to some number of offspring). |
|
Trexler, J.
C., D. L. DeAngelis, and J. Jiang. 2011. Chapter 9. Community assembly
and mode of reproduction: predicting the distribution of livebearing
fishes, pp 95-108. In: Evans, J., A. Pilastro, and I. Schlupp, Eds.
Ecology and Evolution of Poeciliid Fishes. University of Chicago Press.
Trexler, J. C., and D. L. DeAngelis. 2010. Modeling the evolution of complex reproductive adaptations in poeciliid fishes: Matrotrophy and superfetation, pp 231-240. In Uribe, M.C., and H. J. Greer, Eds. Viviparous Fishes II. New Life Publications, Homestead, FL. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C., and D. L. DeAngelis. 2003. Resource allocation in offspring provisioning: an evaluation of the conditions favoring the evolution of matrotrophy. American Naturalist 165:574-585 [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C. 1997. Resource availability and offspring provisioning: plasticity in embryo nourishment in sailfin mollies. Ecology 78:1370-1381 [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J.C., J. Travis, and A. Dinep. 1997. Variation among populations of the sailfin molly in the rate of concurrent multiple paternity and its implications for mating-system evolution. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 40:297-305
Trexler, J. C., R. C. Tempe, and J. Travis. 1994. Size-selective predation of sailfin mollies by two species of heron. Oikos 69:250-258
Trexler, J. C., J. Travis, and M. McManus.1992. Effects of habitat and body size on mortality rates of Poecilia latipinna. Ecology 73:2224-2236. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C., and J. Travis.1990. Phenotypic plasticity in the sailfin molly (Pisces: Poeciliidae). I. Field experiment. Evolution 44:143-156. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C,, J. Travis, and M. Trexler. 1990. Phenotypic plasticity in the sailfin molly (Pisces: Poeciliidae). II. Laboratory experiments. Evolution 44:157-167. [Click here to Download now]
Trexler, J. C. 1989. Phenotypic plasticity in poeciliid life histories. In G. Meffe and F.F. Snelson, Jr. (eds.), Ecology and Evolution of Poeciliid Fishes. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Trexler, J. C. 1988. Hierarchical organization of genetic variation in the sailfin molly, Poecilia latipinna (Pisces, Poeciliidae).
Evolution 42:1006-1017 [Click
here to Download]
Return to FIU Biological Sciences Home Page
Return to Trexler Home Page